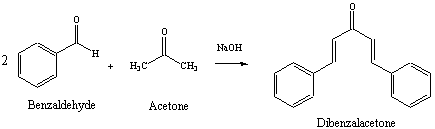
Figure 1: Reaction Scheme for Preparation of Dibenzalacetone
Organic Chemistry Laboratory II
Dibenzalacetone by the Aldol Condensation
Experimental Procedure

Figure 1: Reaction Scheme for Preparation of Dibenzalacetone
The first step of the reaction involves generation of the enolate of acetone, using sodium hydroxide as base. The enolate then reacts with the carbonyl carbon of the benzaldehyde in a nucleophilic acyl addition. A second enolate of acetone is generated which then reacts with another molecule of benzaldehyde. The resulting dibenzalacetone contains a ketone and two alkene functional groups, that are conjugated.
The dibenzalacetone product will be characterized by melting
point and TLC analysis, and the percent yield will be
determinied. The overall purpose of this experiment is to
illustrate the mixed aldol condensation as a way to prepare a,b-unsaturated carbonyl compounds.
 Figure 1: Reaction Set up |
Clamp a 250ml Erlenmeyer
flask to a ring stand and set the flask on a hot
plate/stirrer. Add a magnetic stir bar to the
flask. Weigh out 5g of NaOH (wear gloves!) and add it
to the flask, along with 40 ml of ethanol and 50 ml of DI
water. Stir the mixture until the sodium hydroxide is
completely dissolved. Add 5ml of
benzaldehyde. After the NaOH in the first flask
is completely dissolved, add 1ml of acetone to the
flask. Continue stirring for 5-10 minutes, then add
another 1ml of acetone. A solid will form in the flask
and it may become difficult to stir. Allow the
reaction mixture to stir (or swirl the flask periodically if
necessary) for 20 minutes. After 20 minutes, clamp a 125ml vacuum flask to a ring stand. Insert an adapter and Buchner funnel, fitted with a piece of filter paper, into the top of the flask. Connect the side arm of the vacuum flask to the aspirator vacuum. Turn on the vacuum and wet the filter paper with ~10ml of ethanol. Pour the reaction mixture through the funnel to isolate the solid product (dibenzalacetone) in the Buchner funnel. Break the vacuum and discard the filtrate, leaving the solid in the funnel. Reassemble the vacuum filtration set-up and wash the solid three times with ~50ml of water. Leave the vacuum on for an addition 5-10 minutes to assist in drying out the product. Use a second piece of clean filter paper to press the solid down, squeezing out excess water. Transfer the solid to a 125ml Erlenmeyer flask. Add 10ml of ethanol to the flask. Clamp the flask to a ring stand and set it in a water bath. Warm the mixture gently in the hot water bath until the solid product completely dissolves. Remove the flask from the water bath and cool it, undisturbed, in an ice bath until a precipitate forms. Set up a clean, dry 125ml vacuum flask, fitted with an adapter and Buchner funnel. Clamp the flask to a ring stand. Pour the ethanol/product mixture through the funnel to isolate the solid. Keep the vacuum on for an additional 5-10 minutes to dry the product. Transfer the product to a watch glass and allow it to dry for an additional 15 minutes. |
 Figure 2: Vacuum filtration |
Jones Test |
Set up three small (75 X 12mm)
test tubes in a test tube rack in the hood. Label the test tubes #1-3. Add ~5 mg of the solid
product or 0.25ml of a liquid reagents to each test
tube. Add ~1ml of acetone to each tube. Use test tube #1 for the
product, tubes # 2 for benzaldehyde and tune #3 for
acetone. Add 2
drops of the Jones reagent to tubes #1-3. Observe each tube for an
immediate (2-5 sec) color change and record results.
|
Brady's Test |
Set up three small
(75mm X 12mm) test tubes in a test tube rack in
the hood. Be
sure
that the test tubes are clean and dry. Label the
test tubes #1-3. In test tube 1, place 2 drops of
benzaldehyde, in test tube 2, place two drops of
acetone, in test tube 3 place ~10mg of the product. Add ~2 ml of
ethanol to each tube and vortex to dissolve the
compounds. Add ~2 ml of the Brady’s
reagent to each test tube. Vortex each
mixture and observe each for the formation
of a orange-yellow precipitate or color
change. If no preciptate forms, allow the
tubes to sit for ~15 minutes and observe again. Record
the results. |
Iodoform Test |
Set up a test tube rack containing three, small (75mm X 12mm) test tubes. Label the test tubes 1-3. In test tube #1, dissolve ~5mg of product ~3 ml of dioxane. In test tube #2, add 2-4 drops benzaldehyde dissolved in ~1 ml dioxane and in test tube #3, add 2-4 drops acetone dissolved in ~1 ml dioxane . Vortex the tubes for ~30 seconds. Add 1 ml of 3M NaOH to each tube and vortex again for 30-40 seconds. Add ~2ml of the iodoform reagent to each tube and heat the tubes (clamp them!) in a hot water bath for 2 minutes. If the dark color is dissipated after heating for 2 minutes, add additional iodoform reagent, 5-7 drops at a time, until the dark color remains after heating for 2 minutes. Add 3 ml of distilled water to each tube and allow them to stand for ~15 minutes. Observe each tube for the formation of a precipitate. Record results from each tube. |